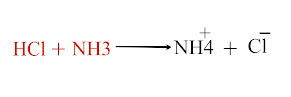Chemistry class 10th Acid Base and Salt MCQs in pakistan Text Book
Chemistry class 10th Acid Base and Salt MCQs in pakistan Text Book According to the Arrhenius concept, which of the following is not and acid a) HCl b) H2SO4 c) CO2 d) HNO3 C is the Correct answer AlCl3 is an acid according to a) Arrhenius b) Lowery and Bronsted c) Lewis d) All of these C is the Correct answer Which of the following is a Lweis base? a) HCl b) AlCl3 c) BF3 d) F negative D is the Correct Answer Neutral solution has a PH value of a) 3 b) 5 c) 7 d) 14 C is the Correct Answer The POH of 0.001M solution of nitric acid is a) 0.001 b) 10.0 c) 11 d) 14 C is the Correct Answer When strong base and weak acid reacts, the only products are a) Neutral salt and water b) Basic salt and water c) Acidic salt and water d) Acidic, basic salt and water b is the Correct Answer NH3 is base according to a) Arrhenius...